本記事では、EdgeYOLOと呼ばれる機械学習手法を用いて、リアルタイム物体検出を行う方法をご紹介します。
EdgeYOLO
概要
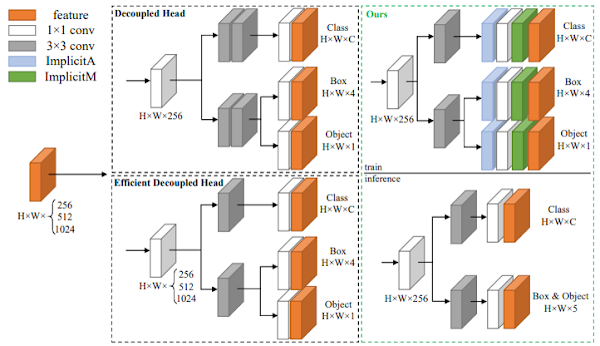
EdgeYOLOは、エッジコンピューティングプラットフォームでリアルタイムに物体を検出可能なアンカーフリーの物体検出技術です。
特徴は、トレーニング中の過学習を抑制するためのデータ拡張方法、小さなオブジェクトの検出精度を向上させるためのhybrid random loss function、FCOSをベースとした軽量で効率的なdecoupled headを備えている点です。
これらにより、精度をほとんど損なうことなく、推論速度を向上させリアルタイム要件である30FPS以上を実現しています。
詳細はこちらの論文をご参照ください。
本記事では上記手法を用いて、動画の物体検出を行います。
デモ(Colaboratory)
それでは、実際に動かしながら物体検出を行います。
ソースコードは本記事にも記載していますが、下記のGitHubでも取得可能です。
GitHub - Colaboratory demo
また、下記から直接Google Colaboratoryで開くこともできます。

なお、このデモはPythonで実装しています。
Pythonの実装に不安がある方、Pythonを使った機械学習について詳しく勉強したい方は、以下の書籍やオンライン講座などがおすすめです。
環境セットアップ
それではセットアップしていきます。
Colaboratoryを開いたら下記を設定しGPUを使用するようにしてください。
「ランタイムのタイプを変更」→「ハードウェアアクセラレータ」をGPUに変更
初めにGithubからソースコードを取得します。
%cd /content
!git clone https://github.com/LSH9832/edgeyolo.git
%cd /content/edgeyolo
# Commits on Feb 28, 2023
!git checkout 673e270917e4db45967b6106585339dd8d7913dd
次にライブラリをインストールします。
%cd /content/edgeyolo
# Install dependent packages
!pip install -r requirements.txt
!pip install moviepy==0.2.3.5 imageio==2.4.1
最後にライブラリをインポートします。
%cd /content/edgeyolo
import os
import time
from datetime import datetime as date
from glob import glob
import cv2
from moviepy.video.fx.resize import resize
from moviepy.editor import VideoFileClip
from edgeyolo.detect import Detector
from detect import draw
以上で環境セットアップは完了です。
学習済みモデルのセットアップ
次に、学習済みモデルをダウンロードします。
%cd /content/edgeyolo
# create directory
!mkdir ./pretrained
# download model
!wget -c https://github.com/LSH9832/edgeyolo/releases/download/v0.0.0/edgeyolo_coco.pth \
-O ./pretrained/edgeyolo_coco.pth
テスト動画のセットアップ
次に、モデルに入力する動画をダウンロードします。
%cd /content/edgeyolo
# create directory
!mkdir ./test_video
!wget -c https://github.com/LSH9832/edgeyolo/releases/download/v0.0.0/test.avi \
-O ./test_video/test.avi
Object Detection
それでは、Object Detectionを実行します。
まず、モデルパスなどを指定します。
WEIGHTS = './pretrained/edgeyolo_coco.pth'
SOURCE = './test_video/test.avi'
CONF_THRES = 0.25
NMS_THRES = 0.5
INPUT_SIZE = [640, 640] # height width
BATCH = 1
SAVE_DIR = './output'
NO_LABEL = False
動画とモデルをロードし推論します。
%cd /content/edgeyolo
# create detecter
detector = Detector
detect = detector(
weight_file = WEIGHTS,
conf_thres = CONF_THRES,
nms_thres = NMS_THRES,
input_size = INPUT_SIZE,
fuse = True,
fp16 = False,
use_decoder = False
)
# load video
source = cv2.VideoCapture(SOURCE)
fps = source.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
print("fps:", fps)
all_dt = []
dts_len = 300 // BATCH
success = True
# start inference
count = 0
t_start = time.time()
while source.isOpened() and success:
frames = []
for _ in range(BATCH):
success, frame = source.read()
if not success:
if not len(frames):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
break
else:
while len(frames) < BATCH:
frames.append(frames[-1])
else:
frames.append(frame)
if not len(frames):
break
# Inference
results = detect(frames, False)
dt = detect.dt
all_dt.append(dt)
if len(all_dt) > dts_len:
all_dt = all_dt[-dts_len:]
print(f"\r{dt * 1000 / BATCH:.1f}ms "
f"average:{sum(all_dt) / len(all_dt) / BATCH * 1000:.1f}ms", end=" ")
# draw detect result
imgs = draw(frames, results, detect.class_names, 2, draw_label=not NO_LABEL)
for img in imgs:
# create save dir
os.makedirs(SAVE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
file_name = f"{str(date.now()).split('.')[0].replace(':', '').replace('-', '').replace(' ', '')}.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(SAVE_DIR, file_name), img)
source.release()
検出結果を描画したフレーム画像を動画に変換します。
det_frames = glob( os.path.join(SAVE_DIR, '*.jpg'))
det_frames.sort()
print('num of frames:', len(det_frames))
h, w, _ = cv2.imread(det_frames[0]).shape
# jpg to mp4
video = cv2.VideoWriter(
os.path.join(SAVE_DIR, 'video.mp4'),
fourcc=cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v'),
fps=float(fps),
frameSize=(w, h),
isColor=True)
for frame_path in det_frames:
img = cv2.imread(frame_path)
video.write(img)
print(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS), (INPUT_SIZE[0], INPUT_SIZE[1]))
video.release()
推論結果は以下の通りです。
# show video
clip = VideoFileClip(os.path.join(SAVE_DIR, 'video.mp4'))
clip = resize(clip, height=420)
clip.ipython_display()
まとめ
本記事では、EdgeYOLOを用いて、動画の物体検出を行う方法をご紹介しました。
動作が軽量になることで、シングルボードコンピューターなどでの適用が考えられます。
また本記事では、機械学習を動かすことにフォーカスしてご紹介しました。
もう少し学術的に体系立てて学びたいという方には以下の書籍などがお勧めです。ぜひご一読下さい。
リンク
リンク
また動かせるだけから理解して応用できるエンジニアの足掛かりに下記のUdemyなどもお勧めです。
参考文献
1.
論文 - EdgeYOLO: An Edge-Real-Time Object Detector
2. GitHub - LSH9832/edgeyolo








0 件のコメント :
コメントを投稿